physical environment
Type of resources
Topics
INSPIRE themes
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
-
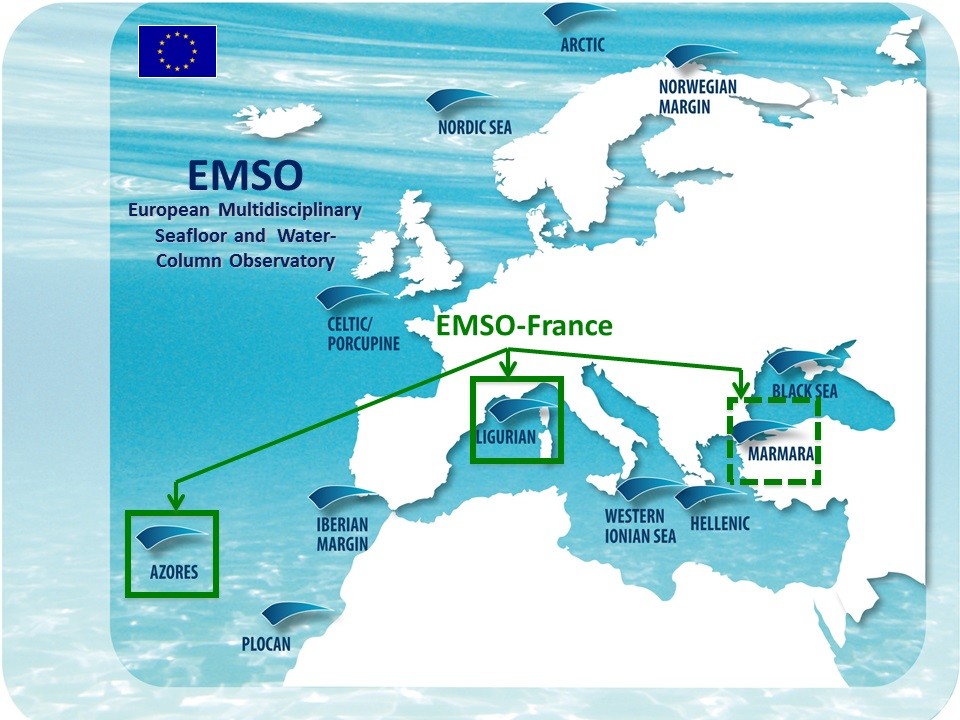
EMSO is a European network of seabed and fixed-point water column observatories whose scientific objective is to acquire long time series in the seas around Europe for the study of environmental processes related to interactions between geosphere, biosphere and hydrosphere. MAREGAMI project (MARine Earthquake Gap Assessment and Monitoring for Istanbul) is a bilateral Turkish-French collaborative project coordinated by IFREMER and Istanbul Technical University and funded by ANR and TÜBITAK. The goal of MAREGAMI is the development of new methods and monitoring strategies to assess earthquake and tsunami risks related to offshore faults, it comprises four tasks: (1) Marine geodesy: acquisition and processing of geodetic submarine data, (2) Hydrodynamics and specific depositional processes: water column data acquisition and hydrodynamic modeling, (3) Improving earthquake relocation with ocean bottom instruments, (4) Designing an optimal and sustainable network of submarine sensors. Data distributed on this portal were acquired for Task 2. The acquisition and distribution of marine data time series in the Sea of Marmara is funded by EMSO-France Research Infrastructure, EMSO-Link, and MAREGAMI projet. DT-INSU provided operational support and instrumentation
-

What drives phytoplankton diversity at fine scales? Phytoplankton diversity is a key component in ocean biogeochemical services and contributes to the resilience and health of ocean ecosystems in respect to local and global stressors, including climate change. Understanding the mechanisms behind phytoplankton diversity in the open ocean is a matter of concern, especially in these years in which large Marine Protected Areas are created in international waters and an international legally binding treaty on Marine Biodiversity Beyond National Jurisdiction is under negotiation. Model studies suggest that finescale ocean dynamics are an important driver of plankton diversity and several scenarios have been suggested. In situ observations however are difficult to perform, due to the ephemeral nature of finescale features and the difficulty of tracking them from available remote sensing. This observational limit will be largely reduced by the SWOT mission, in particular during the fast sampling phase, opening new possibilities to biophysical experiments in the open ocean. The BIOSWOT-Med campaign aims at exploiting SWOT observations for unveiling the drivers of phytoplankton diversity in the Western Mediterranean. The western Mediterranean Sea is characterized by high plankton diversity, low nutrient concentration, and weak oceanic circulation. Here, finescale features, even if weak and short-lived, can strongly modulate the microbial community structure. To study the finescale biophysical coupling, and its impact of phytoplankton diversity, the BIOSWOT-Med campaign will follow the temporal evolution of eddies and filaments over the western Mediterranean SWOT crossover. The physical-biochemical coupling at the frontal zone between Atlantic Water recently entered in the Mediterranean basin and modified Atlantic Water coming from cyclonic circulation in the western Mediterranean basin will be studied through an adaptive Lagrangian sampling strategy using the software SPASSO (Software Package for an Adaptive Satellite-based Sampling for Oceanographic cruises) developed in previous research cruises. This physical information will be paired by a multi-sensor characterization of the planktonic community, including advanced molecular (meta-transcriptomics, metagenomics and meta-barcoding) techniques, and the use of autonomous and robotic platforms. Institutes involved in the campaign: AMU, LOCEAN, CEA, CNR, CNRS, CSIC, Fisheries and Ocean Canada, IFREMER, IRD, MBARI, NWRA, OGS, SHOM, Sorbonne Université, SZN, UCSD, ULCO, University of Exeter, University of Washington.
 OSU Pytheas - Data Catalog
OSU Pytheas - Data Catalog